Your inner ear is perhaps the most important part of your ear.
Your inner ear is perhaps the most important part of your ear. In the inner ear, all of what you hear is transformed. What is it transformed from? Incoming noises and signals, basically what you perceive in the world around you is decoded and interpreted by your brain, processed through the inner ear. In this blog we’ll tell you how best to protect it.
How Does the Inner Ear Even Work?
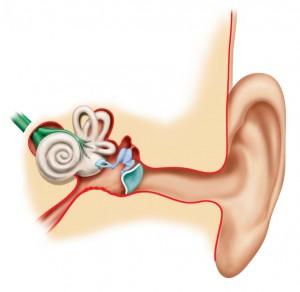
The various parts of your ear work in concert to bring you the pleasure of aural input. Sound, in short. First, the outer ear collects the sound and sends it through the middle ear via the ear canal. The eardrum then comes into play to help the middle ear transfer the sound as kinetic energy. From the eardrum, the sound passes through the middle ear. There are three bones in the middle ear that help pass sound along. These bones are called the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. The bones in your middle ear transform the kinetic energy into wave vibrations.
These wave vibrations then pass along into the inner ear. Inside the inner ear, the cochlea and embedded hair follicles respond to the incoming stimuli. The last step the inner ear performs is to turn these stimuli into electrical impulses, which the brain can use as input. The input is decoded as what we’re actually hearing.
Besides hearing, your inner ears help in another way. Semicircular canals, another feature of the inner ear, help keep all of us balanced. There are three semicircular canals in each of our ears, and these canals all have a liquid that flows as we move around. The ebbing and flowing of liquid in these canals is what helps us stay balanced so we don’t fall over just getting up to walk away from the couch for a tasty snack.
How Do You Best Protect Your Ears?
Protecting your ears is easy! Although you might think your inner ear is safe, since it is deep inside your head, you must still keep it safe through constant vigilance. Use hearing protection when you expect to be exposed to long-term loud noise. The hairs deep inside your ear can be damaged or destroyed extremely easily. The consequences of their damage or destruction will typically be developing hearing loss or titannus.
